Next: 2.2 Exponential Map Up: 2 SO(3): Rotations in Previous: 2 SO(3): Rotations in
Elements of the 3D rotation group,
![]() , are represented
by 3D rotation matrices. Composition and inversion in the group correspond
to matrix multiplication and inversion. Because rotation matrices
are orthogonal, inversion is equivalent to transposition.
, are represented
by 3D rotation matrices. Composition and inversion in the group correspond
to matrix multiplication and inversion. Because rotation matrices
are orthogonal, inversion is equivalent to transposition.
| (1) | |||
| (2) |
The Lie algebra,
![]() , is the set of
, is the set of ![]() skew-symmetric
matrices. The generators of
skew-symmetric
matrices. The generators of
![]() correspond to the derivatives
of rotation around the each of the standard axes, evaluated at the
identity:
correspond to the derivatives
of rotation around the each of the standard axes, evaluated at the
identity:
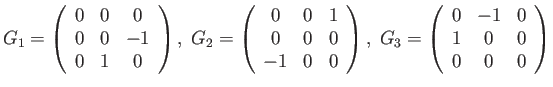 |
(3) |
An element of
![]() is then represented as a linear combination
of the generators:
is then represented as a linear combination
of the generators:
| (4) | |||
| (5) |
We will simply write
![]() as a
3-vector of the coefficients, and use
as a
3-vector of the coefficients, and use
![]() to represent the corresponding skew symmetric matrix.
to represent the corresponding skew symmetric matrix.
Ethan Eade 2012-02-16